Total knee replacement (TKR) surgery success rates vary based on age. Still, the success rate is high, with most patients experiencing significant pain relief and improved knee function. A person’s overall health, knee joint degeneration, and the effect of pain and functional limitations on their quality of life all play a role in determining if they are a candidate for TKR surgery, which has no set age restriction. Many older adults, including those in their 70s, 80s, or even older, have successfully undergone TKR surgeries if they meet specific criteria and are in good health.
Factors affecting the success rates for TKR surgery for various age groups:
- Younger patients(Under 65 years):
- Success rates for TKR surgery in younger patients (under 65) are typically excellent in pain relief and functional improvement.
- Younger patients tend to have better bone quality, fewer comorbidities and are more physically active, which can contribute to a higher likelihood of successful outcomes.
- The prosthetic knee joint may last longer in younger patients.
- Middle-aged patients(65-74 years):
- Middle-aged patients also generally experience favourable outcomes from TKR surgery.
- Success rates in this age group are typically high, and many patients report substantial pain relief and increased mobility.
- However, the longevity of the artificial joint may become a concern in some cases.
- Older patients(75+ years):
- Success rates for TKR surgery in older patients (75 and older) are also quite good.
- These individuals often experience significant pain relief and function improvements, which can significantly enhance their quality of life.
- The primary concern in older patients is the risk of complications due to age-related health issues.
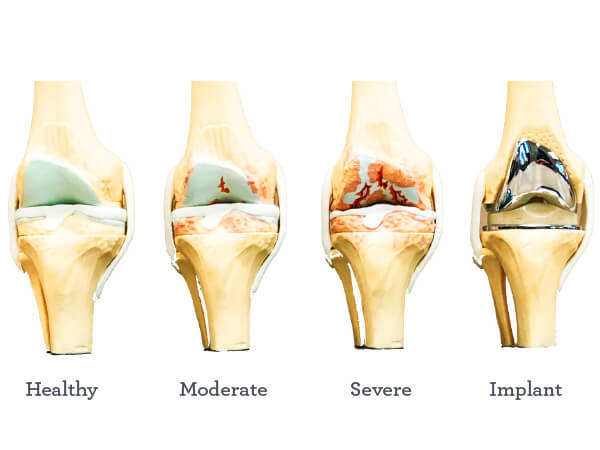
Knee joint replacement (TKR) surgery success depends on the patient’s health, a common condition, surgeon’s skill, and post-operative rehabilitation commitment. Complications, such as infection, blood clots, or implant-related issues, can occur in any age group. Patients should consult their orthopaedic surgeon for personalized advice. Advances in surgical techniques and prosthetic materials have improved success rates, making TKR a reliable option for severe knee arthritis or joint damage.
Precautions and guidelines followed after total knee replacement age-wise:
Following the guidelines and precautions after total knee replacement (TKR) surgery can vary based on age, as different age groups may have different needs. It’s crucial to consult your orthopaedic surgeon and healthcare team for personalized guidance, considering age-wise precautions for daily routine.
For younger age patients(Under 65):
- Follow the rehabilitation plan:
- Be diligent in following your post-operative rehabilitation plan.
- Younger patients often recover faster and may be more physically active, so it’s crucial to regain strength, flexibility, and mobility.
- Return to physical activities:
- As your surgeon recommends, you gradually reintroduce physical activities you enjoy, such as sports or recreational pursuits.
- Ensure you fully regain strength and mobility before engaging in more demanding activities.
- Long-term joint preservation:
- Consider long-term joint preservation strategies, such as maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and avoiding high-impact activities that may stress the artificial joint.
- Adopt to your lifestyle:
- Make modifications to your lifestyle and daily routine to accommodate your post-TKR needs.
- Ensure your work environment and recreational activities are joint-friendly.
For middle-aged patients(65-74):
Balance recovery and daily life:
Find a balance between your post-operative rehabilitation and daily life.
Prioritize regaining function and focus on activities that matter most to you
- Stay active:
- Engage in low-impact activities like walking and swimming to maintain physical fitness and joint health.
- Adopt to work needs:
- If you’re working, consider workplace modifications or accommodations, such as ergonomic adjustments, to ensure a comfortable work environment.
- Diet and nutrition:
- Maintain a healthy diet to support your overall health, including joint health and bone density.
- To maintain healthy bones, make sure you consume adequate calcium and vitamin D.
For older patients:
- Fall prevention:
- Older patients may have an increased risk of falls.
- Make sure your home environment is safe and free from tripping hazards.
- Consider using assistive devices like handrails and grab bars.
- Moderation:
- Be mindful of your energy levels.
- Rest when necessary, and avoid exhausting too much energy.
- Avoid overexertion to prevent fatigue.
- Maintain mobility:
- Focus on maintaining mobility through daily walks and gentle range-of-motion exercises to keep the knee joint flexible.
- Medication management:
- If you have other age-related health conditions, manage your medications diligently and follow your healthcare team’s recommendations.
Regardless of age, all TKR patients should do so:
- Attend follow-up appointments with your surgeon for monitoring and assessment.
- Communicate openly with your healthcare team about any issues or concerns.
- Continue with any prescribed exercises or physical therapy programs.
- Gradually increase your activity levels while avoiding high-impact activities.
Achieving a successful recovery after TKR surgery requires balancing rehabilitation and daily activities, following healthcare team advice to regain function, reduce pain, and enjoy a good quality of life.
Following total knee replacement, you have to stick to the following diet:
After total knee replacement surgery, patients’ dietary needs are generally similar across age groups, focusing on healing, inflammation reduction, and overall health support, with age-related considerations.
- Protein:
- For tissue repair and healing, protein is essential.
- It is essential for rebuilding muscle and other tissues after surgery.
- Include lean protein sources like poultry, fish, lean meats, tofu, and legumes.
- Anti-inflammatory foods:
- Certain foods can help reduce inflammation, which is common after surgery.
- Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., fatty fish, flaxseeds), antioxidants (e.g., berries, leafy greens), and spices with anti-inflammatory properties (e.g., turmeric, ginger).
- Calcium and vitamin D:
- Bone health depends on getting enough calcium and vitamin D in your diet.
- Dairy products, leafy greens, fortified foods, and supplements (if recommended by your healthcare team) can help meet these needs.
- Fiber:
- Fibre aids digestion and can help prevent constipation joint after surgery due to pain medications.
- Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are good sources of fibre.
- Hydration:
- Staying well-hydrated is crucial for overall health and can also help with medication absorption.
- Aim to drink plenty of water and other hydrating beverages, but be mindful of any specific fluid restrictions your healthcare team may recommend.
- Vitamin C:
- Vitamin C is vital for wound healing and collagen formation.
- Don’t forget to eat bell peppers, strawberries, and citrus fruits.
- Iron:
- Iron is essential for carrying oxygen to tissues and promoting energy.
- Include iron-rich foods like lean meats, beans, and leafy greens, especially if you experienced blood loss during surgery.
- Small, frequent meals:
- Smaller, more frequent meals can help digestion and provide a steady energy source and nutrients.
- Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods:
- Highly processed and sugary foods can contribute to inflammation and may not support your recovery.
- It’s a good idea to limit certain foods in your diet.
- Medication considerations:
- If you’re taking blood-thinning medications, discuss with your healthcare team whether there are any dietary restrictions or interactions you need to be aware of.
Dietary considerations connected to age may include:
- Older patients may have specific nutrient requirements, such as adequate calcium and vitamin D for bone health.
- If you have any underlying health conditions or are on a special diet, work with a registered dietitian to tailor your post-surgery diet to your needs.
- Older patients may also consider maintaining an appropriate calorie intake to support energy levels and muscle preservation.
Collaborate with your healthcare team and registered dietitian to create a personalised post-TKR diet plan, considering individual needs and recovery progress, as diet significantly impacts healing and overall well-being post-surgery.
About Dr Anjani Kumar
As an orthopaedic surgeon in Hyderabad, I try to provide patients with as many options as possible for hip and knee treatments to help each patient have the greatest results. I carefully consider the specific sorts of injuries and need to be comfortable offering a specialised solution before recommending the best course of therapy for each patient. My patients’ enhanced mobility and pain reduction are always my top priorities, as these will enable them to resume an active lifestyle. In more severe cases, especially when the joint has collapsed, or the bone has suffered extensive deformation, knee replacement surgery may be advised.
Knee replacement surgery may be recommended in advanced cases, especially if the joint has collapsed or the bone has become severely deformed.
Dr. Anjani Kumar has 20 years of experience and successfully performed 2000 knee replacement surgeries, 350 hip replacement surgeries, and 500 pelvic acetabular surgeries throughout his career. Please get in touch with us on Mobile: at +91 9989112411 and by E-mail: anjanikumar@ gmail.com.