Ligament injuries are frequent and can significantly affect a person’s everyday life and physical health. Ligaments are crucial for holding bones together, supporting joints, and enabling regulated movement. An injury may occur if a ligament is subjected to extreme force, straining, or tearing.
Causes and symptoms of ligament injury:
There are numerous causes and reasons why ligament injuries might happen.
Many things, including sports, mishaps, trauma, and repetitive stress, can bring on ligament injuries. In sports, rapid direction changes, turning, jumping, and collisions with other players can put too much strain on ligaments, causing sprains or tears. Ligament injuries can also result from mishaps or traumatic incidents like slips or auto accidents. Furthermore, abuse of certain joints or repetitive motions might deteriorate ligaments.
Typical causes of ligament injuries:
Trauma: A rapid trauma or a direct hit to the joint frequently causes ligament damage. This can occur during sporting activities, falls, accidents, or any other circumstance where the joint is subjected to excessive force.
Sports-related injuries: Playing sports that require quick stops, abrupt direction changes, jumping, or collision can stress the ligaments and increase the chance of injury. Ligament injuries are more common in sports like soccer, basketball, football, skiing, and tennis.
Overuse or repetitive stress: Long-term repetitive stress on the ligaments might result in injury. Running or leaping repeatedly while not getting enough rest and recovery might stretch the ligaments and increase their susceptibility to injury.
Poor conditioning and muscle imbalances:
Poor training and muscle imbalances can lead to ligament injuries. Especially true for the muscles that support and stabilise joints. Lack of strength, flexibility, or muscle imbalances can put additional strain on the ligaments, raising the risk of injury.
It is significant to highlight that individual factors, including heredity, anatomical variances, and prior traumas, can also contribute to ligament problems. In many instances, the risk of ligament injuries can be decreased by performing a proper warm-up, conditioning, using the right safety equipment, and employing good technique.
Typical symptoms of ligament injuries:
The symptoms of ligament damage can vary depending on the extent and location of the damage. Depending on the scope of the damage, the particular ligament implicated, and individual circumstances, ligament injuries can present with various symptoms. Pain, bruising, swelling, joint instability, difficulty moving the injured joint, and a popping or tearing feeling at the time of injury are typical symptoms. Some people could have trouble lifting weights or carrying out joint-movement-demanding tasks.
Diagnosis and treatment for ligament injuries:
A comprehensive physical examination and imaging tests like X-rays, ultrasounds, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are all necessary for ligament injury. Once the damage has been identified, the best course of action is based on its seriousness.
For minor to moderate ligament injuries, conservative treatment approaches are frequently considered. These may include pain management with over-the-counter drugs, rest, ice therapy, compression, and elevation (RICE protocol). The injured joint may need to be immobilised using braces, splints, or casts to safeguard and stabilise it. Physical therapy is essential for rehabilitation since it focuses on regaining joint stability, enhancing flexibility, and strengthening the muscles around the injured area.
The following are some typical treatments that might be suggested:
Rest and immobilisation: Rest and immobilisation are essential for the initial healing process of an injured joint, as is avoiding activities that worsen the pain. When a joint needs to be stabilised and a brace, splint, or cast is not appropriate, immobilisation may be required, such as using a brace, splint, or cast.
Ice therapy: Ice therapy can assist in lessening pain, oedema, and inflammation in the affected area. Ice packs are applied to the site. In the acute period of the injury, it is typically advised to apply ice for roughly 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours.
Compression: Applying compression bandages or wraps to the torn ligament can help reduce swelling and support it. The reduction should be snug but not so tight to prevent blood flow.
Elevation: By encouraging fluid outflow from the area, elevating the damaged limb above the level of the heart can help reduce swelling.
Pain management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) or over-the-counter painkillers like paracetamol may be suggested to manage pain and reduce inflammation. But before taking any drug, with a medical expert.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy is frequently crucial to treating ligament injuries. A physical therapist can create a unique workout regimen to increase the damaged joint’s strength, flexibility, and stability. They could also apply ultrasound or electrical stimulation to speed up the healing process.
Bracing or tape: Depending on the injury’s severity, a medical expert may advise bracing or taping to give the joint external support. At the same time, it heals during activities that strain the ligament.
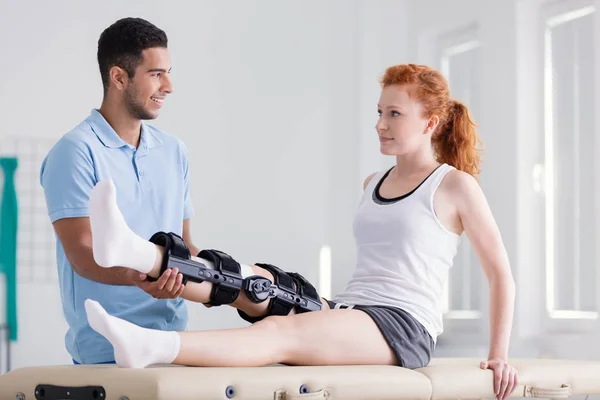

Surgical intervention: Surgery may be necessary for severe ligament injuries, such as total tears or considerable instability. Ligament repair, graft-based reconstruction, and other surgical treatments are available to help the joint regain stability and functionality.
It’s crucial to remember that treatment schedules should be customised for each patient, considering the specific injury, general health, and lifestyle. To get a precise diagnosis and the best treatment advice for your particular ligament damage, speak with a healthcare professional such as an orthopaedic doctor or physical therapist.
Recovery:
Ligament injuries require a gradual and individualised rehabilitation procedure. Recovery times differ based on the extent of the damage, the particular ligament implicated, commitment to treatment and rehabilitation regimens, and personal healing capacities. While less severe injuries and surgical procedures may take many months to a year or longer to heal, mild ligament sprains may recover within a few weeks to a few months.
Rehabilitation is essential to healing because it helps the injured joint regain strength, flexibility, and stability. Exercises, manual therapy, and modalities are frequently used in physical therapy sessions to promote healing, increase range of motion, and regain functional abilities. To guarantee a secure and efficient recovery, competent medical assistance is essential.
Conclusion:
Ligament injuries can significantly influence people’s lives and prevent them from participating in sports and everyday activities. Knowing the causes, symptoms, available treatments, and recovery procedures connected with ligament injuries is essential to guarantee prompt diagnosis, proper care, and successful rehabilitation. Maximising the odds of a full recovery and return to an active lifestyle can be achieved by seeking early medical assistance, adhering to recommended treatment regimens, and actively participating in rehabilitation exercises.
Depending on the patient and the unique circumstances of their accident and treatment, ACL surgery can differ. Always consult your healthcare physician for specific advice on accelerating your ACL healing.
Knee replacement surgery may be recommended in advanced cases, especially if the joint has collapsed or the bone has become severely deformed.
Dr Anjani Kumar has 20 years of experience and successfully performed 2000 knee replacement surgeries, 350 hip replacement surgeries, and 500 pelvic acetabular surgeries throughout his career. Please get in touch with us on Mobile: at +91 9989112411 and by E-mail: anjanikumar@ gmail.com