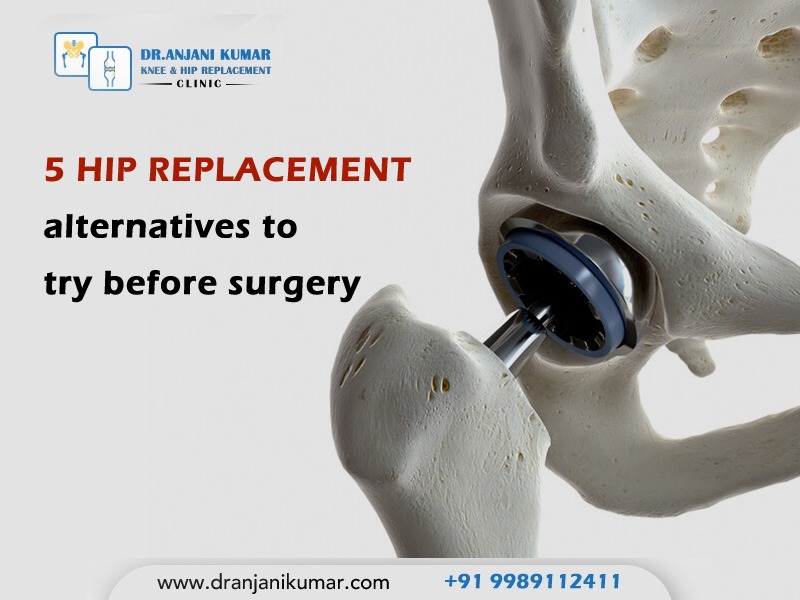
Hip replacement surgery is often recommended for individuals with severe hip pain and limited mobility due to conditions like osteoarthritis or hip fractures. However, non-surgical alternatives can help manage hip pain and improve quality of life. The effectiveness of these alternatives depends on the underlying cause and severity of the hip condition. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific situation.
Non-surgical treatments and lifestyle modifications can potentially prevent hip replacement surgery, depending on the underlying cause of hip pain and the joint damage extent.
5 hip replacement alternatives to try before surgery:
1-Physical therapy
Physical therapy is a customised exercise program to strengthen hip muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance joint function. It is beneficial for various hip conditions like osteoarthritis and muscle imbalances. The effectiveness of non-surgical interventions depends on the individual’s diagnosis. However, surgery may be necessary for advanced or degenerative diseases. The specific program depends on the individual’s condition and recommended non-surgical approach.
- Range of motion exercises: Gentle exercises, including passive and active range of motion, can enhance hip joint flexibility.
- Strengthening exercises: Targeted exercises strengthen muscles around the hip joint, such as hip flexors, abductors, adductors, and external rotators, improving stability and support.
- Core strengthening exercises: Strengthening core muscles, including abdominals, lower back, and pelvic muscles, is crucial for stability, distributing forces evenly, and reducing hip joint stress.
- Balancing exercises: Balance exercises, for instance, standing on one leg or walking heel-to-toe, can enhance proprioception and stability.
- Functional exercises: Walking on uneven surfaces and climbing stairs are suggested to improve functional mobility.
- Stretching exercises: Stretching exercises improve flexibility in muscles around the hip joint, leading to better joint function and reduced pain.

- Joint mobilisation techniques: Physical therapists use manual techniques to mobilise the hip joint and surrounding tissues to improve joint mechanics and reduce stiffness.
- Soft tissue mobilisation: Massage and myofascial release techniques alleviate tension and tightness in the soft tissues surrounding the hip.
- Gait training: Gait training involves analysing and correcting walking patterns to ensure proper gait mechanics, which can reduce stress on the hip joint during walking.
- Aquatic therapy: Aquatic therapy, a form of water-based exercise, offers a low-impact environment that reduces joint stress, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with hip pain.

- Neuromuscular reeducation: Neuromuscular control and coordination can be enhanced through exercises that improve communication between the nervous system and muscles.
- Posture correction: Correcting poor posture can help alleviate hip pain; postural exercises and ergonomic recommendations can be beneficial.
2- Lifestyle modification
Lifestyle modifications can enhance the success of hip replacement methods, manage hip pain, and improve function.
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for hip replacement and managing pain without surgery. It promotes joint health, reduces stress, and improves overall well-being. A holistic approach is essential, considering diet, exercise, and lifestyle. Physical therapists can provide personalised guidance, but professional advice is always sought before starting any weight management program.
Lifestyle changes reduce joint stress, promote joint health, and improve non-surgical interventions. Please consult a healthcare professional before making significant lifestyle changes or exercise programs, especially for managing a hip condition, as they should be tailored to your unique circumstances.
3-Heat and cold therapy
Heat and cold therapy, also known as thermotherapy and cryotherapy, are essential in managing hip pain and hip replacement. They provide relief, improve joint mobility, and enhance comfort. Consult a healthcare provider or physical therapist for guidance on frequency and duration, and exercise caution for individuals with certain circulatory conditions.
Heat therapy(thermotherapy):
Apply heat for 15-20 minutes, using a hot water bottle, warm towel, or heating pad, avoiding direct skin contact and using a cloth or towel as a barrier. The advantages of heat therapy are:
- Increased blood flow: Heat applied to the hip area boosts blood flow, promoting oxygen and nutrient delivery to tissues, aiding in healing and reducing stiffness.
- Muscle relaxation: Heat relaxes muscles, reducing tension and spasms around the hip joint, improving flexibility and reducing discomfort.
- Joint lubrication: Thermotherapy improves synovial fluid viscosity in the hip joint, enhancing joint lubrication, smoother movement, reduced friction, and reduced pain.
- Pain relief: Heat can alleviate discomfort by blocking pain signals and stimulating sensory receptors, providing a soothing sensation and distracting from pain perception.
- Warm-up before exercises: Heat application before physical therapy exercises can enhance the effectiveness of rehabilitation by preparing muscles and joints for movement.
- Relaxation and stress reduction:Heat therapy can promote relaxation and reduce stress, potentially enhancing pain perception and overall well-being.
Cold therapy(cryptotherapy):
Apply cold therapy to the skin using ice packs, cold gel packs, or frozen pea bags wrapped in a cloth, avoiding direct application to the skin.
- Reduced inflammation: Cold therapy reduces inflammation and swelling in hip pain by constricting blood vessels and limiting blood flow to the affected area.
- Numbing effect: Cold packs temporarily relieve pain in the hip area by numbing nerves, particularly after physical therapy or discomfort-causing activities.
- Post-exercise recovery: Cold therapy post-exercise or physical therapy sessions can effectively manage post-exertion inflammation and decrease the likelihood of muscle soreness.
- Local anaesthetic effect: Cold therapy acts as a local anaesthetic, reducing pain in the hip joint and surrounding tissues.
- Reduction of spasms: Cold packs can alleviate muscle spasms, reduce muscle activity, promote relaxation, and ease hip tension by reducing muscle spasms.
4-Assistive devices:
Assistive devices are essential for hip replacement and pain management without surgery. They enhance mobility, reduce joint strain, and provide daily support. Healthcare professionals, like physical or occupational therapists, should guide the use of these devices. They can assess individual needs, recommend appropriate devices, and provide proper usage guidance. Assistive devices are temporary, so individuals should gradually increase mobility as needed.
- Reduced weight-bearing: Devices like canes, crutches, or walkers alleviate hip joint pain by distributing weight, reducing load, and minimising discomfort during walking or standing.
- Improved stability: Assistive devices improve stability, reduce falls, and support balance issues, especially during recovery or managing hip pain without surgery.
- Easier mobility: Canes, crutches, and walkers offer increased stability and mobility, especially for individuals with hip pain or limited mobility.
- Adaptive equipment for daily activities: Assistive devices are adaptive equipment designed to make daily activities more manageable, such as reachers and dressing aids, by reducing strain on the hip joint.
- Crutch or cane use for gait modification: Healthcare professionals can use crutches or canes to modify gait and reduce hip pressure during rehabilitation or non-surgical hip condition management.
5-weight management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for promoting alternative hip replacement methods and managing hip pain without surgery.
Balanced diet:
Maintain a balanced, nutritious diet containing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats while reducing consumption of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-calorie snacks.
Portion control:
To prevent overeating, use smaller plates and bowls and monitor your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
Regular meals and snacks:
Maintain steady energy levels by eating regular, well-balanced meals throughout the day and including healthy snacks to prevent excessive hunger and overeating.
Hydration:
Maintaining adequate water intake is crucial for overall health and weight management, as hunger can sometimes be mistaken for dehydration.
Limit processed foods and added sugars:
Reduce consumption of processed foods, sugary snacks, and beverages as they can lead to excess calorie intake and may not provide necessary nutrients.
Mindful eating:
Slow eating, savouring food, avoiding distractions like TV and electronic devices during meals, and being aware of hunger and fullness cues are all part of mindful eating.
Regular physical activity:
Mindful eating involves slow eating, savouring food, being aware of hunger and fullness cues, and avoiding distractions like TV or electronic devices during meals.
Strength training:
Strength training exercises are essential for building muscle mass, supporting joints, and increasing overall metabolism.
Cardiovascular exercise:
To improve cardiovascular health, it is recommended to engage in 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
Monitor the progress:
Monitor your progress by tracking your eating habits, physical activity, and weight, adjust your approach as needed, and celebrate your achievements.
Consult a dietitian:
Consult a registered dietitian for personalised dietary advice based on your health needs and goals.
Consult your healthcare professional before making significant lifestyle changes or starting a new exercise program to receive personalised guidance based on your specific condition and health goals. Consistent adherence to lifestyle modifications can contribute to the effectiveness of non-surgical alternatives in treatment plans. The particular approach should be tailored to the individual’s condition and needs, and healthcare professionals like physical therapists, nutritionists, and orthopaedic specialists can provide personalised guidance for incorporating lifestyle modifications into a comprehensive non-surgical treatment plan.
Please consult your healthcare professional before making significant lifestyle changes or starting a new exercise program, as they can provide personalised guidance and help develop a plan aligned with your health goals, and consistent adherence to lifestyle modifications can enhance treatment effectiveness.
About Dr Anjani Kumar
As an orthopaedic surgeon in Hyderabad, I provide patients with as many options as possible for hip and knee treatments to help each patient have the most outstanding results. I carefully consider the specific sorts of injuries and need to be comfortable offering a specialised solution before recommending the best course of therapy for each patient. My patients’ enhanced mobility and pain reduction are always my top priorities, as these will enable them to resume an active lifestyle. In more severe cases, especially when the joint has collapsed or the bone has suffered extensive deformation, knee replacement surgery may be advised.
Knee replacement surgery may be recommended in advanced cases, especially if the joint has collapsed or the bone has become severely deformed.
Dr. Anjani Kumar has 20 years of experience and successfully performed 2000 knee replacement surgeries, 350 hip replacement surgeries, and 500 pelvic acetabular surgeries throughout his career. Please get in touch with us on Mobile at +91 9989112411 and by E-mail: anjanikumar@ gmail.com