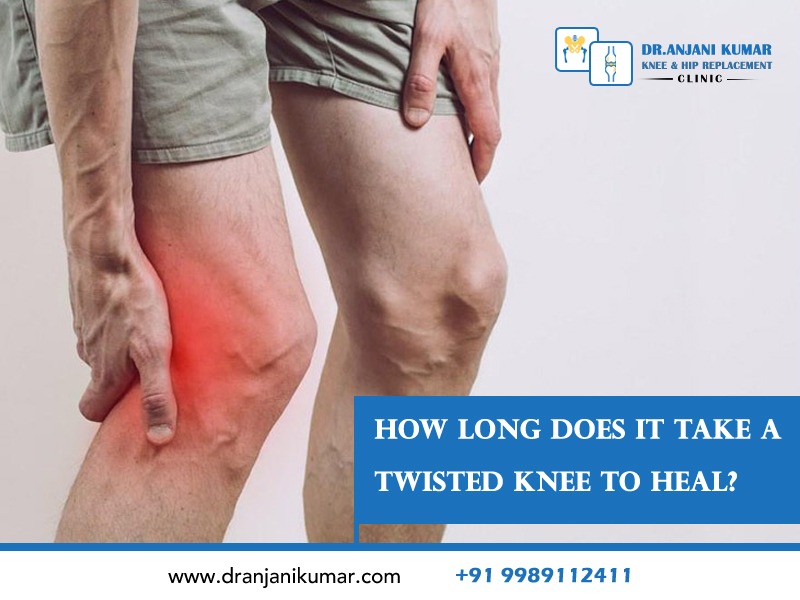
A twisted knee, also known as a sprain or strain, occurs when ligaments or soft tissues surrounding the knee joint are stretched, torn, or injured due to sudden or forceful twisting or rotational movement. The severity of this injury varies from mild to severe, depending on the extent of tissue damage. Commonly affected ligaments include ACL, PCL, MCL, and LCL, causing pain, swelling, and limited range of motion. Recovery time and severity vary based on the degree of ligament or soft tissue damage. Proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing complications and ensuring proper healing. Treatment may include rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and surgical intervention for severe ligament tears. Seeking medical attention from a qualified healthcare professional is advisable to determine the injury’s extent and receive appropriate treatment.
Causes and reasons for the twisted knee:
A twisted knee, also known as a knee sprain, arises from various causes, including:
- Sudden twisting or rotational movements: Twisted knee is a common cause of sudden leg twisting, often caused by sports activities, falls, or accidents.
- Sports injuries: Knee sprains occur with quick direction changes, pivoting, jumping, and sudden stops, with a higher risk in sports like soccer, basketball, and gymnastics.
- Trips and falls: Twisted knees can result from accidents, particularly bent or twisted knees.
- Uneven surfaces: Walking on uneven surfaces increases knee twist risk due to awkward foot landings.
- Overexertion: Excessive knee strain, caused by overexertion or lifting heavy objects, may cause twisted knees.
- Weak muscles and ligaments: Knee joint weakness and lax ligaments increase twisting injury risk.
- Improper footwear: Poor footwear increases knee injury risk, including twists.
- Previous knee injuries: Previous knee injuries or surgeries increase joint vulnerability to twisting due to altered biomechanics or weakened structures.
- Inadequate warm-ups: Improper warming before physical activities increases the risk of muscle and ligament injury.
- Fatigue and overuse: Fatigue and overuse of knee muscles reduce joint stability, increasing twisting risk.
- Anatomic factors: Anatomical factors like leg length and alignment contribute to knee injuries, including twisted knees.
- Age and degeneration: As we age, knee joint ligaments and tissues may become less flexible, increasing injury risk and causing twisting injuries.
Twisted knees can cause severe injuries, like ligament tears or joint damage. Seek medical attention for accurate diagnosis and treatment for knee-related injuries.
Treatment given for twisted knee by doctors:
Treatment for twisted knees varies based on injury severity; doctors may recommend common approaches: rest, medication, and physical therapy.
- Rest: Rest is crucial for knee healing, avoiding weight-bearing activities and high-impact exercises.
- Ice: Ice application reduces swelling and pain in injured areas, lasting 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours for the initial days.
- Compression: Compression bandage controls swelling and supports the injured knee, ensuring a snug yet supportive fit.
- Elevation: Elevating the injured leg above heart level reduces swelling by allowing fluids to drain away from the affected area.
- Pain medications: Doctor may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs for pain management; consult a healthcare professional before use.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy is essential for recovery, utilizing customized exercise programs to improve range of motion, muscle strength, and knee stability.
- Bracing and splinting: A knee brace or splint may be prescribed for stability, support, and healing in injured knees.
- Crutches: Severe knee injury may require crutches for weight relief and mobility.
- Ultrasound or electrical stimulation: Physical therapists use pain relief and tissue healing modalities.
- Corticosteroid injections: Corticosteroid injections may reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Surgical interventions: Severe cases like complete ligament tears require surgery to repair or reconstruct the damaged ligament, depending on the specific ligament and injury extent.
A treatment plan tailored to an individual’s injury, health, and lifestyle is essential. Consult a qualified healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations.
Time taken to recover from twisted knee:
Triceps for twisted knees vary based on injury severity, treatment, health, and rehabilitation plan adherence, with a general timeline for recovery.
- Mild sprain(Grade 1): Grade 1 knee sprain recovery time typically ranges from 1 to 3 weeks, depending on factors like injury severity and individual needs.
- Grade 1 ligament stretching and tissue damage can vary, with minimal damage promoting faster recovery.
- Adherence to treatment plans, including RICE (rest, ice, compression and elevation) and exercises, significantly accelerates recovery.
- Younger, healthy individuals may experience faster healing compared to older or underlying health conditions.
- Gentle range-of-motion exercises and physical therapy improve flexibility and strength and speed recovery.
- For Grade 1 knee sprains, many people can resume normal daily activities relatively quickly, and some may even feel a significant improvement within the first week.
- It’s crucial not to rush back into strenuous activities or sports until you’ve received clearance from a healthcare professional to avoid exacerbating the injury.
For a Grade 1 knee sprain, consult a medical professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment guidance. They can provide personalized recovery recommendations and help manage the healing process effectively.
2. Moderate sprain(Grade 2): Grade 2 knee sprain recovery time is 4-6 weeks, depending on specific ligaments, tissue damage, age, health, and adherence to treatment and rehabilitation plan.
- During the initial week, focus on RICE to reduce swelling and manage pain, using crutches to avoid excessive weight on the injured knee.
- Healthcare providers suggest range-of-motion, physical therapy, and stability exercises for improving swelling, pain reduction, flexibility, and muscle strength.
- The rehabilitation Phase involves intensifying physical therapy for 3-6 weeks to restore strength, stability, and proper knee joint movement patterns.
- Gradual return to activity after knee stabilization, pain relief, low-impact activities, and safe resumes of demanding sports.
- Consult an orthopaedic specialist or sports medicine doctor for personalized guidance, assessment, and treatment adjustments for successful recovery.
3. Severe sprain(Grade 3): The recovery time for Grade 3 knee sprains varies based on factors like ligament type, tissue damage, healing capacity, age, health, and treatment. Typically, it lasts from weeks to months, longer than milder grades.
- The initial phase focuses on pain reduction, swelling, inflammation, RICE, and crutches for 1-2 weeks.
- Acute symptoms improve. Begin gentle exercises, controlled activities, and physical therapy to promote healing and prevent stiffness.
- The recovery phase involves physical therapy, exercises, and surgery for knee injuries.
- Knee healing and muscle strength restoration progress depend on response and assessment.
- Grade 3 sprains are complex, requiring surgical intervention to extend the timeline, particularly if the ligament is torn.
Seek healthcare professionals for personalized recovery time estimates, treatment recommendations, and progress monitoring to ensure clear timelines.
- The specific ligaments or structures affected.
- Age, general health, and level of physical activity of an individual.
- The presence of any underlying medical conditions.
- Adherence to the recommended treatment plan, including rest, physical therapy, and exercises.
- The effectiveness of pain management and inflammation control.
- The type and timing of any surgical intervention, if required.
Consult a qualified healthcare professional for an accurate recovery time estimate, evaluate injury severity, offer personalized guidance, and monitor progress throughout the healing process.
Precautions to be followed for the twisted knee recovery
To promote faster healing and reduce complications in twisted knees, follow a structured approach and take appropriate precautions.
These steps include:
- Rest: Promote knee rest, avoid stress, and avoid high-impact activities.
- Ice: Daily ice application reduces swelling and pain in injured areas.
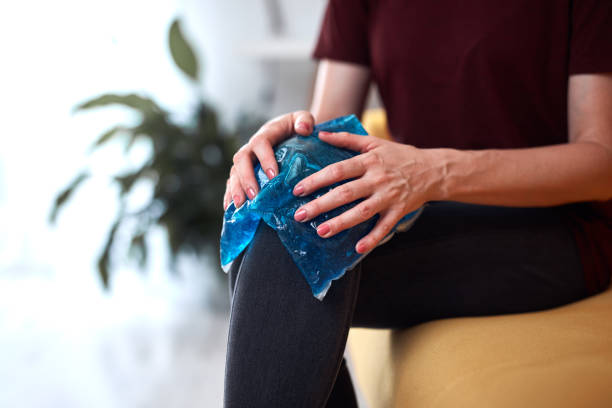

- Compression: Compression bandage manages swelling without affecting blood circulation.
- Elevation: Elevate the leg to reduce swelling and drain fluid.
- Pain management: Consult a healthcare professional before using over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Physical therapy exercises: The healthcare provider recommends gentle exercises for knee healing and function restoration.
- Use crutches or a brace: The healthcare provider suggests crutches or knee braces for weight relief.
- Follow medical advice: Follow the healthcare plan, attend follow-ups, and report progress.
- Avoid aggravating activities: Reintroduce weight-bearing and physical exercise gradually under healthcare guidance.
- Proper nutrition: A balanced diet supports healing and tissue repair.
- Hydration: Adequate water intake is crucial for tissue hydration and healing.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol: Reduce alcohol and tobacco consumption during recovery for better healing.
- Listen to your body: Monitor knee pain and stop if discomfort or swelling occurs.
- Gradual return to activity: Gradually reintroduce physical activities after healthcare approval, starting with low-impact exercises.
About Dr Anjani Kumar
As an orthopaedic surgeon in Hyderabad, I try to provide patients with as many options as possible for hip and knee treatments to help each patient have the greatest results. I carefully consider the specific sorts of injuries and need to be comfortable offering a specialised solution before recommending the best course of therapy for each patient. My patients’ enhanced mobility and pain reduction are always my top priorities, as these will enable them to resume an active lifestyle. In more severe cases, especially when the joint has collapsed, or the bone has suffered extensive deformation, knee replacement surgery may be advised.
Knee replacement surgery may be recommended in advanced cases, especially if the joint has collapsed or the bone has become severely deformed.
Dr Anjani Kumar has 20 years of experience and successfully performed 2000 knee replacement surgeries, 350 hip replacement surgeries, and 500 pelvic acetabular surgeries throughout his career. Please get in touch with us on Mobile: at +91 9989112411 and by E-mail: anjanikumar@ gmail.com