Twisted knees are common among athletes, individuals with weak or unstable knees, overweight or obese individuals, and women due to their naturally weaker knees. These individuals are more susceptible to injury due to age, genetics, and previous knee injuries. Twisted knees result from sudden changes in direction or twisting motion of the knee joint, causing pain, swelling, and instability. The best way to diagnose and treat twisted knees is crucial to see a doctor who can diagnose the extent of the injury and recommend the best treatment. Most cases can be treated with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), but surgery may be necessary in some cases.
Symptoms of the twisted knee:
Common twisted knee symptoms include:
Pain: Twisted knee causes immediate or delayed joint pain, ranging from mild to severe.
Swelling: Knee swelling may result from injury-induced inflammation, causing swelling within hours or days, causing a more prominent knee appearance.
Bruising: Twisting force causes blood vessel rupture, causing knee bruising with discolouration or bluish-purple skin.
Instability: Twisted knee causes instability, noticeable when standing, walking, or bearing weight on the affected leg.
Limited range of motion: Knee joint pain and swelling may limit the range of motion, making it difficult to bend or straighten.
Tenderness to touch: Knee joint tenderness may cause pain when touched or pressured.
Difficulty walking: Difficulty walking or bearing weight on the injured leg may cause pain; crutches or assistive devices may be needed.
Consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment of knee symptoms, including other injuries or conditions, through physical examination, imaging tests, and treatment plans.
Treatment for the twisted knee:
Treatment for twisted knees depends on injury severity and affected structures.
Common treatments for the twisted knee are:
Rest: Rest the knee after injury to prevent further damage and initiate healing.
Ice: Apply ice packs to injured knees for 15-20 minutes daily, and wrap in thin cloth for skin protection.
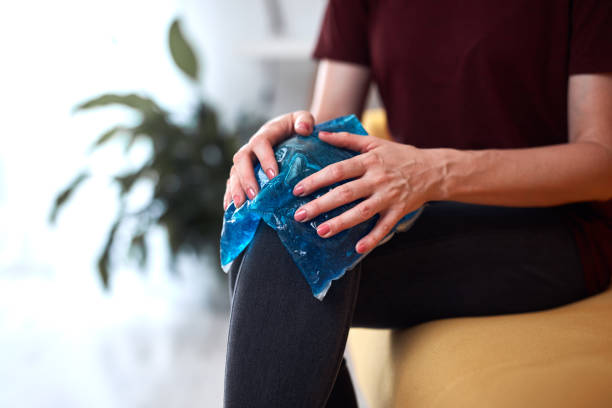

Compression: Knee compression reduces swelling, supports joints, and ensures snugness without affecting circulation.
Elevation: Elevating knees above heart level reduces swelling and promotes fluid drainage.
Pain management: NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen help manage pain, but follow the dosage and consult a healthcare professional.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy aids knee joint rehabilitation by guiding exercises, techniques, and modalities like ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or manual therapy to restore strength, flexibility, and stability.
Bracing: A knee brace or supportive device is recommended for injury severity and healing structures.
Surgical intervention: Surgery may be necessary for severely twisted knees with ligament tears, structural damage, or high-stability activities.
Consult a healthcare professional like an orthopaedic specialist or sports medicine physician to assess injury severity and determine a treatment plan for the twisted knee. They can provide a thorough evaluation, order imaging tests, and guide your situation’s most suitable course of action.
Precautions to be taken for the twisted knee:
Warm-up and stretching: Warm-up and stretching before physical activities improve flexibility and reduce injury risk, including twisted knees.
Use proper techniques: Learn proper techniques for sports, including proper body mechanics, appropriate form, and avoiding excessive force or overexertion during movements.
Wear proper footwear: Proper footwear offers support, cushioning, stability, and activity-specific design to reduce knee risk and improve traction.
Strengthen leg muscles: Strengthen leg muscles, especially quadriceps and hamstrings, to improve knee joint stability and reduce injury risk. Engage in squats and lunges for targeted exercises.
Maintain good balance and proprioception: Engage in exercises to improve balance and proprioception, enhancing joint stability and reducing falls and knee missteps.
Use protective equipment: Protect knee joints in high-risk sports with knee braces or pads for added support.
Avoid over-exertion and fatigue: Avoid overexertion and fatigue by pacing, listening to your body, and taking breaks to prevent accidents and injuries.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces knee joint stress and prevents twisting injuries.
Be cautious on uneven surfaces: Exercise caution on uneven surfaces to avoid missteps, falls, and knee twisted knees.
Listen to your body: Listen to your body for knee joint pain and discomfort; ignore warning signs to prevent injury and prolong recovery time.
Precautions reduce twisted knee risk, but accidents still occur. Seek medical attention for evaluation and treatment if sustained.
Who suffers the most from a twisted knee?
Twisted knee affects all ages and activity levels; factors increase risk, with certain groups more prone.
- Athletes: Sports that involve sudden changes in direction, pivoting, or high-impact movements put athletes at a higher risk of experiencing a twisted knee.
- Sports like soccer, basketball, football, skiing, and gymnastics often involve such movements, making athletes in these sports more susceptible.
- Active individuals: Even those who participate in recreational activities or fitness exercises requiring quick direction changes or jumping movements can be at risk of a twisted knee.
- Individuals with previous knee injuries: If you have previously experienced knee injuries, such as a torn ligament or cartilage damage, the stability of your knee joint may already be compromised.
- Consequently, you are more likely to suffer further knee injuries like twisted knees.
- Weak muscles and poor flexibility: Weak thigh muscles (quadriceps and hamstrings) and poor leg muscle flexibility can affect the knee joint’s stability.
- When these supporting structures are weak, it increases the risk of twisting the knee during certain movements.
- Improper footwear: Wearing shoes without adequate support or wearing worn-out soles can increase the risk of knee twisting.
- Proper footwear that provides stability and cushioning is essential, especially during sports or activities that involve running, jumping, or quick changes in direction.
Factors like accidents falls, and tripping can increase the risk of a twisted knee, but anyone can sustain the injury under specific circumstances. Forceful twisting can occur at various ages and activity levels.
About Dr Anjani Kumar
As an orthopaedic surgeon in Hyderabad, I provide patients with as many options as possible for hip and knee treatments to help each patient have the most significant results. I carefully consider the specific sorts of injuries and need to be comfortable offering a specialised solution before recommending the best course of therapy for each patient. My patients’ enhanced mobility and pain reduction are always my top priorities, as these will enable them to resume an active lifestyle. In more severe cases, especially when the joint has collapsed, or the bone has suffered extensive deformation, knee replacement surgery may be advised.
Knee replacement surgery may be recommended in advanced cases, especially if the joint has collapsed or the bone has become severely deformed.
Dr Anjani Kumar has 20 years of experience and successfully performed 2000 knee replacement surgeries, 350 hip replacement surgeries, and 500 pelvic acetabular surgeries throughout his career. Please get in touch with us on Mobile: at +91 9989112411 and by E-mail: anjanikumar@ gmail.com




